A.Projects
1. Ongoing
a. Enhacing patien



Safety care pamphlet
Patient safety promotion video
Patient safety information as L-shape file folder
t engagement in patient safety
b. Identifying caregiver burnout and improving the resilience
Adapting “Enhacing Caregiver Resilience: Burnout & Quality Improvement Protocol” by Duke University Health System Patient Safety Center, it is expected that the work pressure of our staffs would relieve and the psychological state of mind would bloom.


c. High-Fidelity, Simulation-based Team Resource Management (TRM) Training
Training started in 2010 and is provided to physicians and nurses from Emergency Department, Intensive Care Unit, medical ward as well as the surgery team. After initiating the very first TRM class in 2007, we aim to bring all the knowledge and skills into the practice on the floor via simulation in order to enhace the teamwork and patient safety.
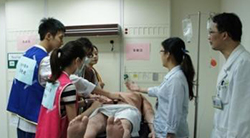
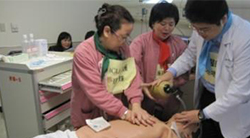

Orientation
Drill
Video Debriefing
2.Major Achievement
a. CAD patient process improvement
By applying six sigma and implementing several improvement steps, the median door-to-balloon time < 90minutes is reached. Furthermore, 90% percent of CAD patients with door-to-balloon time less than 90 minutes, which is better than the 75% as recommended by the American Heart Association (AHA).
b. Blood transfusion safety
After analysing the risks of blood transfusion process, the all-in-one PDA was used to streamline the blood transfusion process, which reduce the human errors to the minimal.



Patient identification check
Blood product check
Blood request check
c. Chemotherapy safety
To evaluate risk and vulnerability in the chemotherapy process using a proactive risk analysis method, Healthcare failure mode and effect analysis (HFMEA) was adopted to identify potential chemotherapy process failures. Computerized physician order entry was adopted to eliminate potential risks in chemotherapy processes. Te errors of chemotherapy were totally eliminated.
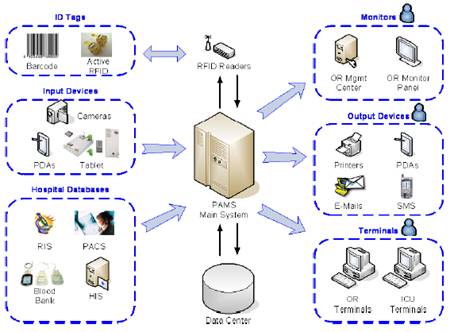
d. RFID in surgical patients
In order to improve management competency and to enhance patient safety, we in-cooperate radio-frequency identification (RFID) and web-based database technologies to develop a Patient Advancement Monitoring System (PAMS) in the operation theater. The RFID-initiated PAMS provides caregivers’ instant, wireless information sharing with minimized data entry work loading. The alert and error-prevention functions of PAMS enhance protection of patient safety and improve quality monitoring. Managers are able to execute real-time, on-line management decisions to further improve operation theater utilization efficiency. The data captured can be analyzed to monitor surgical quality from risk and outcome perspectives.
e. Central line bundle care implementation
By implementing central line bundle care program, we introduced 5 evidence-based interventions, the catheter-related bloodstream infections (BSIs) rate at our ICUs has dropped and maintained at the rate of 6‰ and 3.6‰ for medical and surgical ICU, respectively.
f. Surgical specimen handling safety
An automatic clinical pathology tracking system (ACPTS) is establishmed after re-engineering surgical specimen handling workflow. The ACPTS contains four functional features, including logistic registration and tracking of surgical specimens, automatic bar-code tag generation, security control of the database and security control of refrigerator.
B. Research
Effectiveness of High-Fidelity, Simulation-based Team Resource Management (TRM) Training - A Controlled Trial
National Science Council, Executive Yuan, NSC 102-2511-S-281-001, Aug. 2013- July 2014
Early Prediction Model via Physiological Variation and Illness Severity Index to the Prognosis of Critical-ill Patients in ICU
CGH-MR-B10205, Sep. 2013-Aug. 2014
One New Training Program of Team Resource Management in Healthcare: Adverse Event Reporting System Implanted Simulation in situ
100CGH-FJU-20, Aug. 2011- July 2012
High-Fidelity Simulation Team Training for Critical Care Medicine – Patient Safety Education in Practice
NSC 101- 2511-S-281-001, Aug. 2012- July 2013
Development and Evaluation of a Clinical-LOSA to Assess the TRM and Technical skills in Emergency and Critical Care Teams
101-CGH-FJU-19, Aug. 2012- July 2013
Investigation of Oral Health-related Quality-of-life Questionnaire
CMRI-9802, Jan. 2009-Dec. 2009
Continue Advanced Team Resource Management Technique to Improve Patient Safety Culture in Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
CMRI-9803, Jan. 2009-Dec. 2009
Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture in Taiwan – Development and Application of a Hospital Patient Safety Culture Scale
DOH96-TD-M-113-027 March 2007-Feburary 2009
Investigation on the Instrument Losses in Operation Room Setting with an Aim to Reduce Its Loss Rates
CMRI-9609, Aug 2007 –July 2008
Analysis of Total Implantable of Central Venous Access Devices via Cephalic Vein
CMRI-9613, Dec 2007 –Nov 2008
Using Web-based Database to Improve Quality in Joint Replacement Management
CMRI-9614, Dec 2007 –Dec 2008
Establishment of Patient Safety Culture in Radiology Department at Cathay Healthcare System
CMRI-9617, Dec 2007–Dec 2008
Establishment of Patient Safety Culture in Pharmacy Department at Cathay Healthcare System
CMRI-9623, Dec 2007–Dec 2008
Use of CRM Technique to Improve Patient Safety Culture in Emergency and Intensive Care Unit
CMRI-9624, Dec 2007–Dec 2008